How Robotic Screw Machine Works | Automated Screw Driving Systems
| Product Name | Applicable industries |
| Dual Head Screwdriver | Consumer Electronics Assembly |
Video Explainer: How a Robotic Screw Machine Works
In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, achieving precision, speed, and consistency is paramount. One technological marvel that stands at the forefront of this revolution is the robotic screw machine. This sophisticated piece of automation is engineered to handle the intricate and repetitive task of screw driving with unparalleled accuracy, transforming assembly lines across countless industries. But how does it actually work? Let’s dive into the mechanics and intelligence behind these remarkable systems.
The Core Components
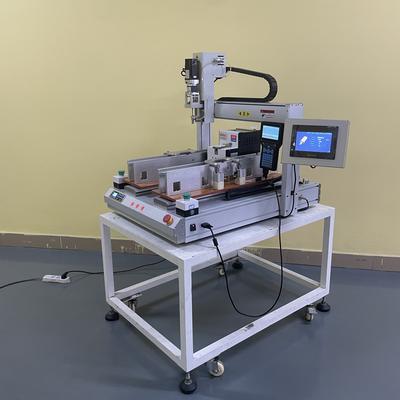
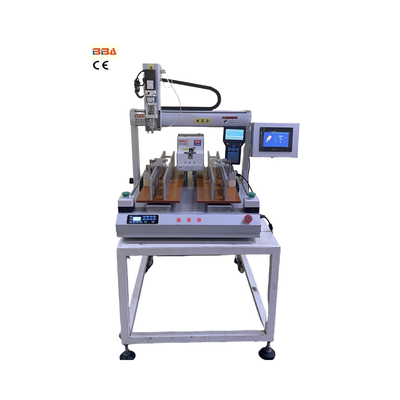
At its heart, a robotic screw machine is an integrated system comprising several key components that work in perfect harmony. The primary elements include a high-precision robotic arm, a specialized screw feeding system, a vision system or sensor array, and an electric screwdriver or spindle attached to the robot's end-of-arm tooling.
The process begins with the screw feeding system, often a vibratory bowl feeder or a flexible tape feeder. This component is responsible for orienting and supplying individual screws in the correct position. From there, a vacuum or mechanical pickup system, mounted on the robotic arm, securely collects the screw.
The Precision Driving Process
Once the screw is acquired, the pre-programmed robotic arm maneuvers it to the exact target location on the assembly product. This is where advanced technology truly shines. An integrated vision system or multiple sensors first identify and confirm the precise hole location and orientation, making micro-adjustments to account for any potential misalignment in the product itself.
The electric screwdriver then engages, driving the screw into place with a predetermined torque value. This closed-loop torque control is critical, as it ensures every screw is fastened perfectly—neither too loose, which could cause product failure, nor too tight, which could strip the threads or damage the component.
Intelligence and Integration
What separates a modern robotic screw machine from a simple automated tool is its embedded intelligence. These systems are typically controlled by sophisticated software that allows them to seamlessly integrate into a broader automated production cell. They can communicate with other machinery, such as conveyors or part placement robots, to receive work orders and send confirmation signals upon task completion.
Furthermore, they are equipped with extensive data logging capabilities. Every screw driven is recorded along with its torque value, providing invaluable data for quality control and traceability. This data can be used to predict maintenance needs, identify process improvements, and ensure consistent product quality throughout the entire production run.
Transformative Benefits for Modern Manufacturing
The implementation of a robotic screw machine offers a multitude of transformative benefits. It dramatically increases production speed and throughput while eliminating the variability and fatigue associated with manual labor. This leads to a significant reduction in errors and product defects, ensuring higher overall quality.
Moreover, it allows human workers to be upskilled and redeployed to more complex, value-added tasks that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills, thereby improving job satisfaction and operational efficiency. The machine also enhances workplace safety by taking over a repetitive task that can lead to musculoskeletal injuries for human operators.
In conclusion, the robotic screw machine is a pinnacle of automation engineering. It combines mechanical precision with digital intelligence to perform a fundamental assembly task with superhuman levels of speed, accuracy, and reliability. As manufacturing continues to evolve towards smarter, more connected factories, the role of such automated workhorses will only become more central, driving productivity and quality to new heights.